Parts of a Tractor – Essential Components of Farm Tractors & Their Functions
Parts of a Tractor – Understanding the Essential Components of Farm Tractors
Introduction
Tractors are valuable assets for agriculture, construction, and other heavy work tasks. Powerful machines of this kind are intended to undertake several activities, such as tilling, plowing, planting, and hauling. Learning how a tractor functions is essential to understanding its parts and components. This guide is dedicated to explaining each tractor part along with its function to aid in understanding the operation of the machinery and how to take care of it.
This guide is designed for anyone who owns a farm tractor or is just interested in learning more about heavy machinery. It covers all significant and essential components of farm tractors, including how they function to improve productive farming activities.
Primary Components of a Tractor
Many parts on a tractor that function together to provide power, control, and efficiency benefits to the user. The following highlights the parts of a tractor and their respective roles:
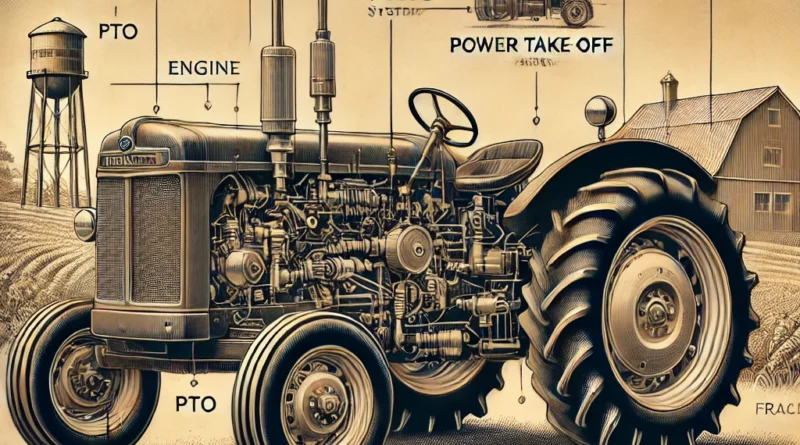
1. Engine
The engine is the primary component of a tractor since it produces power to propel the vehicle and operate the attachments on the tractor. Most diesel tractors utilize diesel engines because of their long life, high fuel economy, and ability to produce massive torque. Important constituents of a tractor engine include:
• Cylinder block – Contains the cylinders in which fuel combustion occurs.
• Piston and crankshaft – Transform the energy from burning fuel into motion.
• Fuel injection system – Supplies fuel into the combustion chamber.
• Cooling system – Controls overheating of the engine by maintaining an optimal temperature.
2. Transmission System
The transmission system transfers power from the engine to the wheels. This lets the tractor move forward or backward while varying the speed and torque. This system comprises:
• Gearbox – Has different sets of gears that speed up or slow down the vehicle.
• Clutch – Connects and disconnects the power to be transmitted.
• Differential – Smoothly divides the power to the wheels for movement.
3. Hydraulic Mechanism
The hydraulic system propels fluid-powered attachments and farming implements, vital in raising, lowering, or operating equipment. The crucial components are:
• Hydraulic pump – Develops the pressure of the fluid.
• Hydraulic cylinders – Regulates structural movements of the attachments.
• Control valves – Manage the rate of fluid movement.
4. Power Take-Off (PTO) Shaft
As an essential component of farming tractors, the PTO shaft transfers power from the tractor to implements such as mowers, balers, and tillers. The PTO efficiently uses implements without needing additional power sources.
5. Steering System
The steering system allows the precise movement of the tractor. The system contains:
• Steering wheel – Gives the operator the ability to set the vehicle’s direction.
• Tie rods and linkage – Connect the steering mechanism and the operating wheels.
• Hydraulic power steering – A feature of newly built tractors for ease of control.
6. Braking System
The braking system lets the operator slow down or stop the tractor ably. It comprises of:
• Mechanical brakes – Generally drum or disc brakes that give the stopping force.
• Hydraulic brakes – A feature of new models that enhances the stopping capacity.
• Parking brake – Locks the tractor while it’s not working.
7. Tires and Wheels
For traction and stability, tractors are fitted with larger rear wheels and comparatively smaller front wheels. The type of tires depends on the tractor’s purpose:
* Agricultural tires – These have deep treads designed for maximum grip on farmland.
* Industrial tires – These are used in construction sites where they endure rough use.
* Turf tires – Specialized for areas requiring minimal soil disturbance.
8. Chassis and Frame
The chassis is the geometric framework of the tractor, which defines the locomotive’s functionality. It guarantees robust durability and stability, particularly during heavy-duty work.
9. Fuel System
This system is responsible for storing fuel and delivering it to the engine. It consists of the following:
* Fuel tank – where diesel or gasoline is stored
* Fuel pump – transfers fuel to the engine
* Fuel filters – to protect engine components by removing impurities.
10. Electrical System
Tractors depend on the electrical system for starting, lighting, and other components. This includes:
* Battery – used for powering the electrical system when starting the engine
* Alternator – electricity generator while the tractor is working
* Starter motor – switches on the engine when the key is turned.
11. Exhaust System
This system of components extracts the exhaust gas from the engine, which consists of:
• Muffler – Minimizes sound.
• Auger pipe – Moves exhaust away from the user.
12. Operator’s Cabin (Cab or ROPS)
The operator’s cabin is designed to be comfortable and safe for the driver. There are two principal kinds:
• Open ROPS (Roll Over Protective Structure) – A protective brace for the operator during rollovers.
• The closed cab protects against environmental conditions such as weather and dust; it also has air conditioning and comfortable seats.
Additions and tools associated with tractors
A tractor can accommodate a range of different implements, which enhances its functionality. Following are a few typical tools that attach to the engine of tractors:
1. Plow
Used to prepare land by turning the top soil in readiness for planting.
2. Harrow
Used in breaking soil clods and smoothing the surface.
3. Seeder
An implement for planting seeds automatically.
4. Mower
Used for harvesting grass and hay to feed livestock.
5. Baler
A machine that packs and fastens hay or straw into bales.
6. Sprayer
A powered implement for applying insecticides or fertilizers to plants.
7. Loader
It is a machine for elevating and shifting loose materials such as dirt, sand, stone, or gravel.
8. Backhoe
An equipment for digging purposes that has a shovel.
Important Practices Regarding the Maintenance of Tractor Parts
In an attempt to maintain reasonable operational efficiency for your tractor, you should consider the following maintenance procedures:
1. Check Fluids Regularly
Review the levels of engine oil, coolant, hydraulic fluid, and transmission oil for adequacy.
2. Tire Check
Inspect the tires for reasonable wear, proper inflation, and alignment to avoid losing balance.
3. Change Air/Fuel Filters
Remove the air and fuel filters as their dirt collects on them to enable the filters to perform at the optimal level.
4. Relubrication of Moving Parts
Ensure reliable lubrication on bearings, joints, and linkage bars.
5. Check All Electrical Wiring
Examine all the wires for slack that could lead to wires touching and causing failures or burnt wires that do not work.
6. Conduct system tests on brakes and steering
Confirm the brakes work as ordered and the steering is functional.
The Bottom Line
Familiarity with tractor parts or components aids an individual in deepening their understanding of any required maintenance, operating the tractor efficiently, and intelligently selecting or repairing farm technologies. Each part of the tractor works in conjunction with the others, and as such, they need to be maintained regularly to guarantee durability and reliability.
Understanding the components of a farm tractor aids farmers and agricultural workers in choosing the most suitable implements and maintaining the devices for maximum productivity. This is essential for those using compact tractors for a small-scale farm or even those using more powerful machines for large implement requirements. Understanding tractor parts will improve your operations and extend the working life of your equipment.